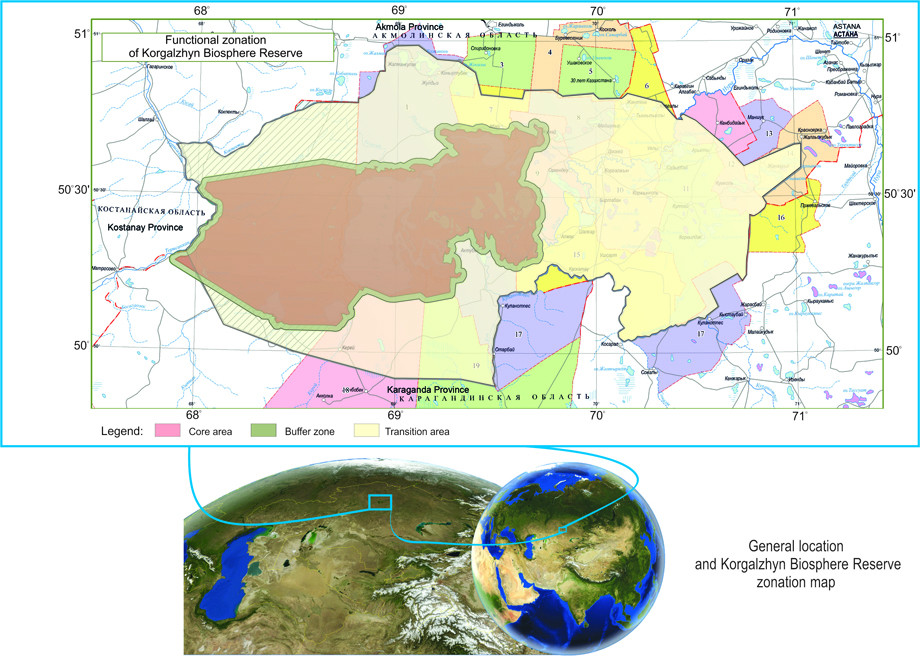
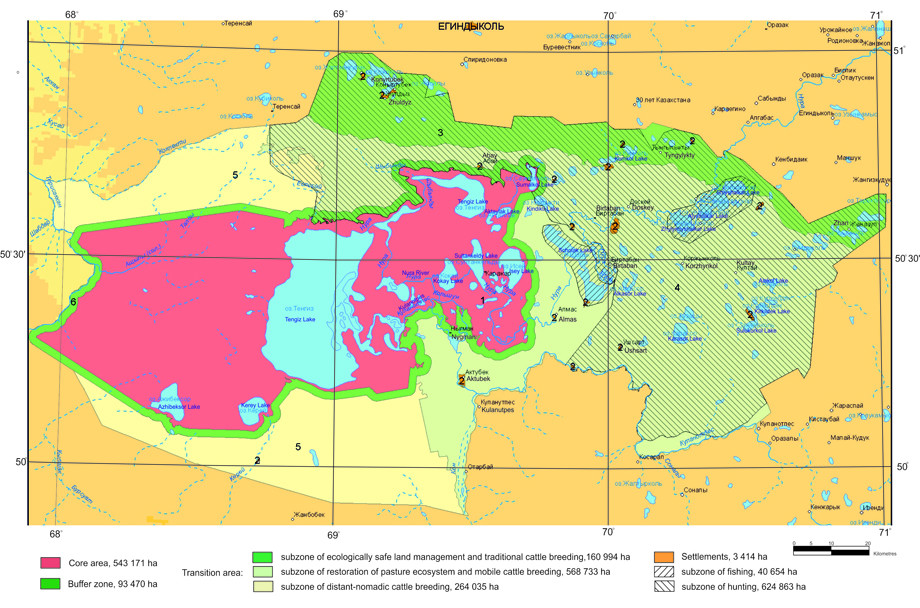
Total area of the territory of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve is 1,603,171 ha. The main core zone (territory of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve) is 543,171 ha, buffer zone is 90,000 ha (a 2-km stripe around the State Nature Reserve), development zone – about 970,000 ha.
The main zone of Biosphere Reserve is strictly protected zone of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve, which represents natural complex of fresh and saline water reservoirs with their coastal territories. According to Article 39 Chapter 7 of the Law of RK «On specially protected natural territories», State Nature Reserve is a specially protected natural territorywith the status of nature protective and scientific institution, its activities' goal is in conservation and research of natural processes on its territory, objects of plandt and animal world, separate species and communities of plants and animals, typical and unique ecological systems and their rehabilitation. At specially designated areas which don't include specially valuable ecological systems and objects it is allowed (according to the order established by authorized body) to create excursion paths and routes for regulated ecological tourism (Article 42). Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve corresponds to the highest category (A1) of nature territories of IUCN. The area of the main nature reserve zone of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve is 534,171 ha.
Buffer zone of Biosphere Reserve is protected zone of State Nature Reserve which consists of 2-km stripe along the state nature reserve's perimeter. According to Article 43 of Law of RK «On specially protected natural territories» protected zones are created for the protection from unfavourable external influences around specially protected natural territories, with prohibition of any activity in the limits of these zones that would negatively influence the condition and restoration of ecosystems of given territories. At the territory of Biosphere Reserve the lands of buffer zone are not confiscated from the main land users, they are mostly formed of the lands of agricultural use and are owned by agricultural organizations and private bodies. Economic activity in separate areas of protected zone (haymaking, cattle pasture) is carried out in accordance with governmental authority (Forestry and Hunting Committee of the Ministry of Agriculture of RK) and under the control of administration of State Nature Reserve. Activities of ecological education, recreation, ecotourism are carried out at the territory of the buffer zone of Biosphere Reserve, as well as scientific research. The area of protected zone is 90,000 ha.
Transition area of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve is located on the territory of three administrative regions and two districts (oblast): Korgalzhyn and Egindykol (Akmolinskaya district) and Nura region (Karagandinskaya district). This zone includes lands of 19 rural districts; its total approximate area is about 970,000 ha. This zone contains 19 forestries and 10 fishing ponds in long-term possession of 15 land users.
The territory of transition area of Biosphere Reserve is used for hayfields, fallow lands, pastures, numerous wetlands and villages. It represents mainly settled and developed areas. It is important to organize restoration of renewable resources at these territories. First of all it concerns the rehabilitation of abandoned fallow lands and organization of sustainable fishery and hunting.
In order to attract the corresponding partners Coordinational Council of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve was created, including representatives of State Nature Reserve, land users, local authorities and non-governmental organizations. Besides, before that there were Territorial Council of Management of Wetland Resources of Tengiz-Korgalzhyn Territory (in the limits of the GEF/UNDP Wetlands Project, 2004 – August 2011), and extended Scientific and Technical Board of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve.
According to the legislation of RK the management of economic activity at separate areas of protected zone (haymaking, cattle pasture) is conducted by agreement with governmental authority (Forestry and Hunting Committee) and under the control of administration of State Nature Reserve, all controversial issues are solved at the sessions of Coondinational Council of Biosphere Reserve. Agreements with land users about collaborative activities on the lands of protected zone were signed during preparation of the Resolution on protected zone of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve. Private lands of buffer zone are not confiscated from land users; this zone consists of agricultural lands administered by agricultural organizations.
At the present time there is a Management Plan for Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve, which describes management of the main and buffer zone of Biosphere Reserve. Land users have their own management plans, which are is accordance with State Nature Reserve's Management Plan. So, simple combination of all these plans is in fact Overall Integrated Management Plan of the whole territory of Biosphere Reserve. A special management plant of Biosphere Reserve including transition area is not created yet, because at this stage of Biosphere Reserve development there is no need in it. All controversial issues are discussed at the sessions of Coordinational Council of Biosphere Reserve.
Management of Biosphere Reserve is conducted through Coordinational Council of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve, created in 2011. Before that the territory was managed by Territorial Council of Management of Wetland Resources of Tengiz-Korgalzhyn Territory and extended Scientific and Technical Board of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve (from 2008 to August 2011). Coordinational Council is a collegial public body and is created with the goal of introduction of effective management and sustainable use of Biosphere Reserve’s resources, introduction of alternative activities, resource-conserving and resource-renewing technologies. Coordinational Council of Biosphere Reserve, with members from governmental agencies (territorial management of forestry and hunting, district territories management of fishery, “Astana su” state republican enterprise), State Nature Reserve, city administration (Akimat)(department of land resources, department of agriculture, etc.), local NGOs and land users, is also important in promoting collaboration and solving controversial issues between all stakeholders.
Currently on the territory of Biosphere Reserve a program of Monitoring of fauna and flora condition, as well as ecosystem's condition is carried out. The goal of this monitoring is to obtain regular objective data on the condition of plants and animals on the territory of Biosphere Reserve, and also on the condition of their habitat. Based on the data of monitoring it is necessary to conduct current evaluation of population and ecosystems’ condition, effectiveness of Biosphere Reserve’s functioning, and also development of measures of prevention (termination) of emergencies and unfavourable situations. Avian countings of population of large waterbirds (Swans, Flamingos, Pelicans, etc.) and Wild Boar are carried out in the limits of monitoring.
Besides, there is current research in State Nature Reserve dedicated to 5 scientific topics: «Passerines of Korgalzhyn Nature Reserve» (fauna, biology, population number), «Rare, disappearing and globally important bird species of Korgalzhyn Nature Reserve and adjacent territories», «Characteristics of ichthyofauna of lakes of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve», «Anseriformes of Korgalzhyn Nature Reserve» (species composition, biology, character of residence), «Nature Chronicles». Also in the nearest future it is planned to conduct research of populations' condition of rare and Red Data Book species – Saiga, Bobak Marmot, White-headed Duck, Demoiselle Crane and Common Crange, as well as Gyrfalcon, Black-winged Pratincole, Black-tailed Godwit and Eurasian Curlew.
The work on ecological education is carried out in visit center (Korgalzhyn village) on the base of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve. It is conducted by the department of ecological education of Nature Reserve. The goal of this work is to form ecological competence of the people, their understanding of the key role of the protected territory, importance unique nature conservation, public support, and raising patriotism and responsibility for the environment and, as the result, decrease of anthropogenic press from local people on region’s biodiversity.
Korgalzhyn Bioshpere Reserve is a natural complex of fresh and saline waters with their coastal territories which include unique landscapes characteristic for dry steppe zone of Eurasia. The territory of the Reserve is a place where unique model areas of natural steppe ecosystems, degraded in other parts of Kazakhstan, are conserved. The territory of Biosphere Reserve is one whole area located in the steppe zone of Central Kazakhstan at the crossing of Central Asian – Indian and Siberian – Eastern-African birds migration routes. It also is an important wetland of international importance not only for Kazakhstan, but for the whole Asia. Spacious waters of Biosphere Reserve provide the necessary habitat for the largest in Asia waterbirds' population.
Potential fodder reserves of only one Tengiz lake are able to provide food for 15 million birds. The most Northern nesting population of Flamingo is located here; its population number in some years may reach 50,000-60,000 birds. This is why in 1974 Tengiz-Korgalzhyn lakes (which are part of the Biosphere Reserve) were included in Ramsar list of internationally important wetlands. The unique Tengiz Lake, as well as its shores, was never anthropogenically influenced; in 2000 this lake was included in the list of Live Lakes international organization, which consists of the most unique lakes of the world. In 2007 this territory also became a part of the world network of sites proved to be extremely valuable for birds' conservation (Important Bird Area).
In 2008 a part of the Reserve's territory (Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve) in nomination «Saryarka – steppes and lakes of Northern Kazakhstan» was included in the List of World Heritage Sites of UNESCO. Before it was included in UNESCO list, the Government of Kazakhstan increased its territory more than twice. The majority of adjoined territory is occupied by steppe area Western from Tengiz Lake which has a high international nature proteciton status – conservation of steppe biom of the planet as a habitat for some steppe mammal species. Here are some favorite habitats of Corsac Fox, Steppe Pika and Saiga, as well as large colonies of Marmot. Besides, this area is important for conservation of steppe bird’s fauna; here is the nesting place of such rare species as Steppe Eagle, Pallid Harrier, Pallas’s Sandgrouse, Demoiselle Crane, Great and Little Bustard. All these species of mammals and birds are listed in the Red Data Book of Kazakhstan and Red List of IUCN. The importance of Biosphere Reserve in local Saiga population conservation is especially noteworthy. In 1970-80s huge flocks of these steppe antilopes came to this not populated steppes every year in early May to have offsprings. According to the data of last years’ surveys, more than 1600 Saigas are annually counted on Biosphere territory, and some part of them stays for the winter.
In a whole, biodiversity of this territory includes more than 500 species of plants (a quarter of the whole flora of Kazakh melkosopochnik) and more than 1400 species of water and terrestrial animals, consisting of 42 mammal species, 14 fish species and 344 bird species (126 of them are nesting). Waterbirds of Tengiz-Korgalzhyn lakes (territory of Biosphere Reserve) include 112 species, which is 87% of total waterbird fauna of Kazakhstan. To the present date more than 700 species of insects is recorded there, although their species diversity may reach more than 3000 species.
More than 60 rare species of animals and plants, listed in the Red Data Books, are registered at the territory of Biosphere Reserve. For example, 37 bird species are listed in the Red Data Book of Kazakhstan and 20 species – in IUCN Red List. Up to 10% of world population of Dalmatian Pelican (IUCN Red List) and up to 10-20% of world population of White-headed Duck is concentrated at Biosphere Reserve’s lakes. During summer molt and autumn migration a huge number of birds (tens of thousands of Geese, hundreds of thousands of Ducks and Sandpipers) may be found at the spacious and rich in fodder waters of the territory.
The territory of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve is situated on the land of 13 rural districts, which are included in 3 areas of 2 regions (oblast) – Egindykol (Akmolinskaya region), Korgalzhyn and Nura (Karagandinskaya region). More than 12,000 people in total live at this territory in 28 settlements. Besides state nature reserve, more than 20 land users are registered here. Potential productivity of agricultural lands is low, the region is a zone of risky agriculture, this is why crop production is not perspective here. Productive landscapes of Biosphere Reserve located near strictly protected nature territory are suitable for cattle keeping, fishery, and hunting and ecological tourism development. Farms were chosen during functional zoning of Biosphere Reserve’s territory to carry out works on sustainable agriculture methods on their basis.
Animal breeding. Cattle population in all farms’ categories (according to the data of 2005) is 13,300 animals, containing 7,600 sheep, 5,000 horses, 665 pigs, and 24,600 birds. 99% of the cattle are owned by local people and farms. In the last 5 years there is a tendency of stable decrease of cattle and birds’ population. The development of agrarian sector at Biosphere Reserve’s territory is caused by the traditions, experience in sheep and horses breeding in extreme conditions of all-year pasture, considerable demand for sheep and horse’s production, proximity of Nur-Sultan (the main market), high prices for meat production at Kazakhstan’s internal market.
Fishery. A part of water reservoirs of biosphere territory are owned by 10 nature users who practice commercial fishery. Average annual yield of fish is 519 tons, of which only 178 are registered by nature users; the other 341 tons are not registered. Due to the increasing demand for fish productions it is necessary to organize activity for restoration and sustainable development of fish resources. Biosphere Reserve allows successful solving these problems in the frames of its Coordinational Council.
Hunting. Hunting farms of Biosphere Reserve's territory include agricultural lands (arable and fallow lands), steppe lands (pastures, hayfields), and wetlands. At the present time paid sites of temporary residence are created for the hunters visiting hunting farm for a long time; necessary staff of rangers and game managers is hired; and also normative documentation is introduced for better counting of game animals taken from the nature.
Ecological tourism. Modern territory of Biosphere Reserve was used for ecological, educational, tourist and recreational purposes from 1996. In the present time 4 ecological routes are developed in protection zone for educational excursions. Due to long routes only vehicles are used, provided by “Akmolatourist” company (tourist buses with 36 and 24 sitting places, 2 microbus, one of them is off-road vehicle), as well as vehicles of State Nature Reserve. The routes lie on the field roads of common use in protected zone with defined places for stops and halts. All vehicles are obligately accompanied by state inspectors of nature reserve’s security service. A lot of time is dedicated to educational excursions for schoolchildren of local regions and Nur-Sultan city; these excursions follow a short program of one-day acquaintance with nature attractions of Biosphere Reserve. In the present time a tourist base is created at “Karazhar” cordon, and a visit center was recently built and opened in Korgalzhyn village.
To the present date the main scientific-technical support of Biosphere Reserve's territory is provided by the staff of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve, “Rodnik” public association, and participants of GEF/UNDP Project on Conservation of Wetlands, which supports pilote projects on folk craft, ecological education and knowledge propaganda; Conception of ecological tourism in Biosphere Reserve is developed; Conception of sustainable fishery at the territory of Birtaban-Shalkarskiye lakes is developed; a series of educational seminars for local people, school teachers and scientific staff was conducted.
In the limits of activity of Korgalzhyn State Nature Reserve (besides the main activity at the Reserve's territory): 1) on the base of visit center – ecological excursions, nature protection activities, ecological festivals, organization of ecological clubs, and advertising - publishing activity, work with mass media, etc.; 2) education of local hunting inspectors to properly conduct counting works; 3) educational – field pratices of students; 4) collaborative activity with emergency service of Korgalzhyn village in steppe fires extinguishing; 5) conduction of scientific research and monitoring of nature condition at Biosphere Reserve’s territory.
In the limits of «Rodnik» public assiciation – creation of 5 guest houses, development of 3 ecological routes; work with tourists; conduction of educational seminars for local people; help in conduction of ecological events and activities on the territory.
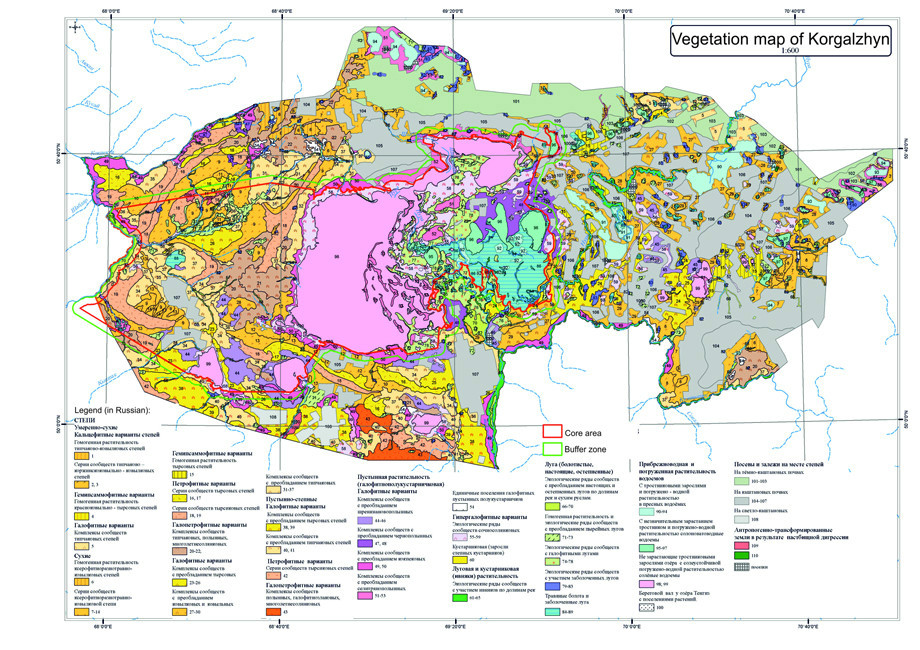
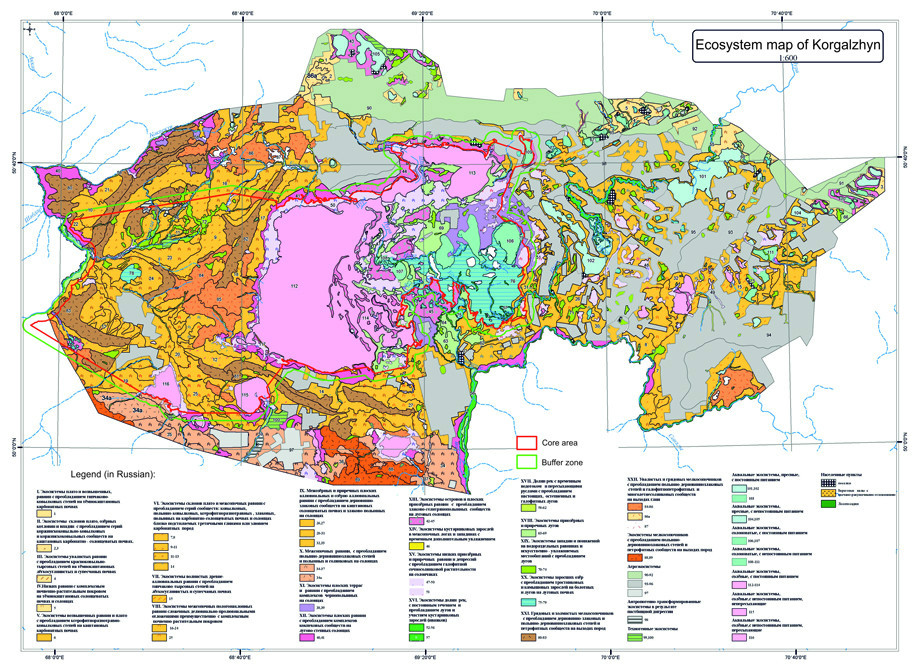
Biosphere Reserve plays an important role in conservation of natural complexes of unique and characteristic ecosystems of dry steppe zone of Eurasia and includes the whole spectrum of dry steppe ecosystems. According to botanic-geographical subdivision the territory of Biosphere Reserve is situated in Euro-Asian steppe region, Zavolzhsko-Kazakhstan province, Central Kazakhstan steppe subprovince, Priishimskiy (Northern and Eastern parts of Biosphere Reserve) and Western - melkosopochnik (Southern part of Biosphere Reserve) districts. According to zonal features the territory of Biosphere Reserve lies in 3 subzones of steppe zone: in subzone of moderately dry steppes on dark-chestnut soils, subzone of dry steppes on chestnut soil and subzone of desertified steppes on light-chestnut soils.
The territory of Biosphere Reserve presents a unique complex of biodiversity of Kazakhstan dry steppe, which is not observed out of the limits of the Republic. Flora of higher plants in Biosphere Reserve is represented by 511 species from 270 genera and 70 families; the base of floristic diversity is created by angiosperm plants (404 species of dicots and 105 species of monocots). Massive (dominant and subdominant) species form 16.6% (85 species from 25 families) from the whole flora, and rare species – 9% (46 species), 5 of them (Tulipa schrenki, T. patens, Adonis wolgensis, Pulsatilla flavescens, P. patens) are listed in the Red Data Book. Floristic relicts include 4 species (Nitraria schoberi, Marsilea strigosa, Nymphaea candida, Nuphar lutea), endemics are represented by 7 endemic and 3 subendemic species.
Fauna of vertebrate animals is represented by 422 species; the majority of them are birds (347 species). The territory of Biosphere Reserve is habitat for 11 endemic and 22 relict vertebrate species, as well as for 67 species from the Red Data Book of Kazakhstan and IUCN, and only from birds globally important species include Dalmatian Pelican, White-headed Duck, Lesser White-fronted Goose, Red-breasted Goose, Gyrfalcon, Demoiselle Crane, Little Bustard, Great Bustard, White-tailed Eagle, Golden Eagle, Imperial Eagle, Steppe Eagle, Pallid Harrier and other birds. The territory of Biosphere Reserve is habitat of the largest in Asia waterbirds' complex, which counts 112 species. The largest stop of migrating birds happens here twice a year. Total one-time number of nesting waterbirds reaches 500,000 specimens. Birds from the huge territory – Northern and Central Kazakhstan, Western and Eastern Siberia – gather for summer molt.
The Reserve is very important for conservation of Central Kazakhstan Saiga population, which was a commercial species in 1970-80s and rapidly decreased in numbers at the end of XXth century. Biosphere Reserve is of huge importance for conservation of species diversity of raw materials’ plants. So, more than 220 medicinal plants, 98 nectariferous and 48 dying plants are recorded here. Almost half of local flora are fodder plants (231 species).
Productive landscapes are convenient from cattle breeding point of view, as well as fishery and hunting. At the same time, some parts of Biosphere Reserve need rehabilitation of abandoned lands. In regional scale the experience of ecological tourism development on the territory of Biosphere Reserve may be successfully used at other sites. In the present time 15 pilot projects are realized at the territory of Korgalzhyn Biosphere Reserve, they are directed mostly on introduction of the best practices in agriculture (sustainable management of pastures), as well as ecotourism development – 5 projects. A project on milk products processing is realized, as well as introduction of the best fishing practices, creation of pond farm and a project in hunting area, one of the project is aimed to demonstrate the alternative energy sources.
